What are integrated circuits?
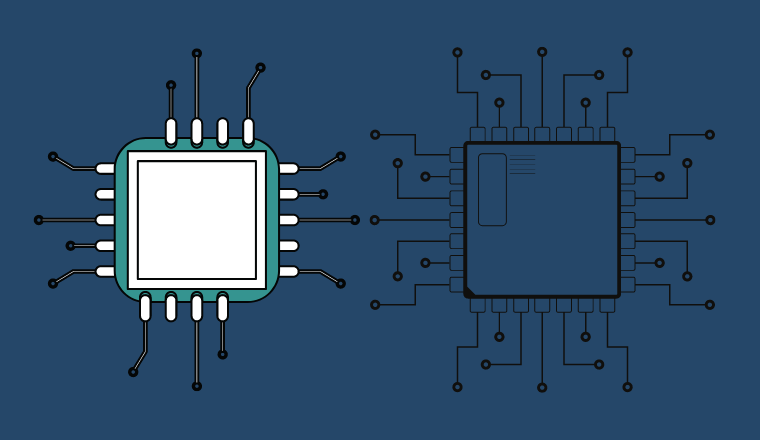
An integrated circuit is a subset of electronic engineering that is made up of electronic components commonly known as microchips. They are also described as miniaturized electronic components used in microprocessor fabrication and composed of many electronic components forming a single unit.
Integrated circuits are commonly made up of 3 layers of electronics namely:
- Wafer: These are thin slices of semiconductors, for example, crystalline silicon (c-Si), and are used for the fabrication of integrated circuits. They are also the foundation of the chip where the electronic components are integrated upon.
- The electronic components: These are etched onto semiconductors and their primary functionalities are to regulate and manage the electrical signals that flow on the chip. They are categorized into active components, such as transistors and diodes, and passive components, such as capacitors and resistors.
- Insulators: These are materials that do not allow heat or electricity to pass through.
- Integrated Circuit Protector (ICP): This is a device installed to protect the integrated circuit from overcurrent. Overcurrent is described as an excess amount of electricity that passes through the conductor, and which can cause excess heat generation fire and damage to the device. ICPs can quickly shut off the device if an overcurrent occurs, which protects the device.
- Aluminum coating: Aluminum is used for its corrosion resistance properties.
What is an Integrated Circuit Topography?
Integrated Circuit Topographies (ICT) refers to a type of integrated circuit that is three-dimensional in its general configuration. They are found in products that utilize integrated circuits or layout designs such as smartphones or products that use electronic functionalities. A three-dimensional integrated circuit (3D IC) is made of a Metal-oxide semiconductor (MOS). It is manufactured in such a fashion that it acts as a single unit, ultimately achieving better performances, and is more power-efficient than its two-dimension IC counterpart. In addition, they also allow for complex electronic functionality to be applied in smaller-sized products.